Understanding Warehouse Inventory in Mexico
Warehouse inventory management plays a crucial role in Mexico's growing logistics and manufacturing sectors. As businesses expand operations across the country, understanding how inventory systems function within Mexican warehouses becomes essential for operational efficiency. This article explores the fundamentals of warehouse inventory practices, regulatory considerations, and practical approaches used throughout Mexico's diverse industrial landscape.
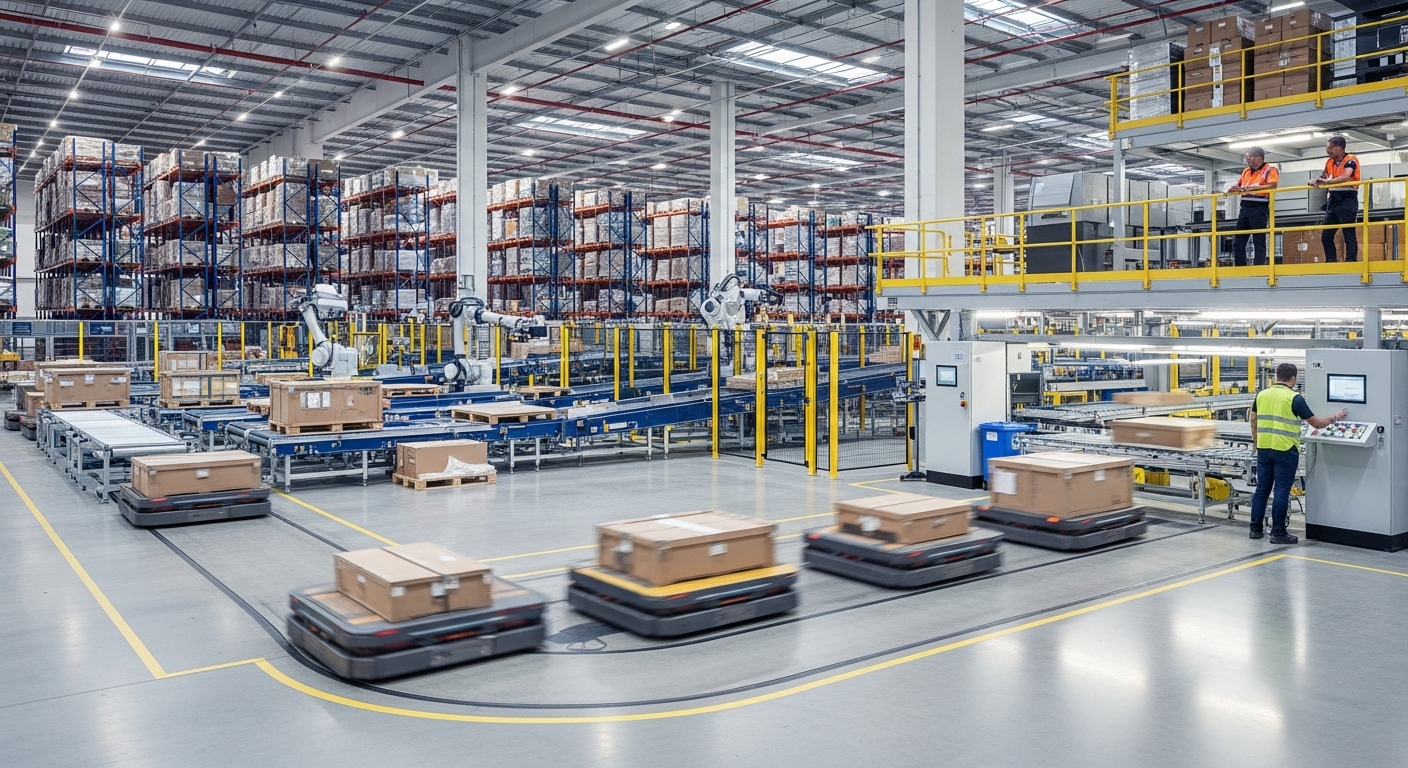

Warehouse Inventory in Mexico Explained
Mexico has emerged as a significant manufacturing and distribution hub in North America, particularly following trade agreements that have strengthened cross-border commerce. Warehouse inventory refers to the systematic tracking, storage, and management of goods within storage facilities. In Mexico, this process involves compliance with local regulations, integration with customs procedures for imported goods, and adaptation to regional infrastructure variations. Companies operating warehouses must maintain accurate records of stock levels, product locations, and movement patterns to ensure smooth supply chain operations.
The Mexican warehouse sector serves various industries including automotive, electronics, textiles, and consumer goods. Inventory management systems range from traditional manual tracking methods in smaller facilities to sophisticated automated solutions in large distribution centers. Understanding the local business environment, including labor practices, technology adoption rates, and regional differences, helps organizations optimize their inventory strategies.
How Warehouse Inventory Works in Mexico
Warehouse inventory operations in Mexico follow established logistics principles while accommodating specific local requirements. The process typically begins with receiving goods, which may arrive from domestic suppliers or through international shipments requiring customs clearance. Upon arrival, items are inspected, documented, and assigned storage locations based on factors such as product type, turnover rate, and handling requirements.
Inventory tracking methods vary by facility size and technological capability. Barcode scanning systems have become standard in medium to large warehouses, while radio-frequency identification technology is increasingly adopted in modern facilities. Smaller operations may still rely on paper-based systems or basic spreadsheet tracking. Regardless of the method, accurate documentation is essential for regulatory compliance and operational efficiency.
Storage strategies in Mexican warehouses often reflect the specific needs of the industries they serve. Cross-docking arrangements are common in facilities supporting just-in-time manufacturing, particularly in automotive clusters near the northern border. Temperature-controlled storage is essential for food and pharmaceutical products, while hazardous materials require specialized handling and segregated storage areas.
Cycle counting and periodic physical inventories help maintain accuracy between recorded and actual stock levels. Many facilities conduct regular audits to identify discrepancies, prevent shrinkage, and ensure data integrity. These practices are particularly important when warehouses handle goods under customs bond or temporary importation programs.
Regulatory Framework and Compliance
Warehouse operations in Mexico must comply with regulations administered by various government agencies. The Tax Administration Service oversees inventory records for tax purposes, requiring businesses to maintain detailed documentation of stock movements. Companies must track inventory values, apply appropriate accounting methods, and report holdings accurately.
For warehouses handling imported goods, understanding customs regulations becomes critical. Mexico operates several customs regimes that affect inventory management, including temporary importation programs that allow manufacturers to bring in materials duty-free for processing and re-export. Warehouses participating in these programs must maintain meticulous records demonstrating compliance with program requirements.
Safety regulations also impact warehouse inventory practices. The Ministry of Labor and Social Welfare establishes workplace safety standards that affect how goods are stored, handled, and moved within facilities. Proper training, equipment maintenance, and hazard communication protocols are mandatory components of compliant warehouse operations.
Technology and Inventory Management Systems
Technology adoption in Mexican warehouse operations has accelerated in recent years, driven by competitive pressures and the need for greater efficiency. Warehouse Management Systems provide integrated platforms for tracking inventory, managing orders, and optimizing storage space. These systems can interface with enterprise resource planning software, transportation management platforms, and customer ordering systems to create seamless information flow.
Cloud-based inventory solutions have gained popularity among Mexican businesses, offering scalability and accessibility without requiring substantial upfront infrastructure investment. Mobile devices enable real-time data capture on the warehouse floor, improving accuracy and reducing paperwork. Some advanced facilities incorporate automated storage and retrieval systems, though manual operations remain common across much of the sector.
Data analytics capabilities allow warehouse managers to identify trends, forecast demand, and optimize stock levels. Predictive analytics can help prevent stockouts or overstock situations, both of which carry financial consequences. Integration with supplier systems enables better coordination and more responsive replenishment processes.
Regional Considerations and Infrastructure
Mexico’s geography and infrastructure development create regional variations in warehouse inventory practices. Northern states benefit from proximity to the United States border and well-developed transportation networks, making them attractive locations for distribution centers serving North American markets. Central Mexico, particularly the Bajío region, has seen substantial warehouse development supporting automotive and aerospace manufacturing clusters.
Transportation infrastructure quality affects inventory strategies, with some regions experiencing longer lead times or less reliable delivery schedules. Warehouses in areas with infrastructure challenges may maintain higher safety stock levels to buffer against supply chain disruptions. Conversely, facilities in well-connected locations can operate with leaner inventories due to more predictable replenishment.
Security considerations also influence warehouse inventory management in Mexico. Facilities implement various protective measures including controlled access, surveillance systems, and security personnel. Inventory tracking helps detect theft or unauthorized removal of goods, while proper documentation supports insurance claims if losses occur.
Best Practices for Effective Inventory Management
Successful warehouse inventory management in Mexico requires attention to several key practices. Establishing clear standard operating procedures ensures consistency in how goods are received, stored, picked, and shipped. Regular training keeps warehouse staff updated on procedures, safety requirements, and system usage.
Maintaining optimal stock levels balances the costs of holding inventory against the risks of stockouts. Analysis of historical demand patterns, seasonal variations, and lead times informs reorder points and safety stock calculations. Collaboration with suppliers and customers improves forecast accuracy and enables more responsive inventory adjustments.
Physical organization of warehouse space directly impacts inventory efficiency. Logical product placement based on movement frequency, compatibility, and handling requirements reduces picking time and minimizes errors. Clear labeling, organized aisles, and designated zones for different product categories or storage conditions support smooth operations.
Continuous improvement efforts help warehouses adapt to changing business needs and incorporate operational lessons. Regular performance measurement using metrics such as inventory accuracy, order fulfillment rates, and space utilization identifies opportunities for enhancement. Benchmarking against industry standards provides context for evaluating performance and setting improvement targets.
Understanding warehouse inventory management in Mexico requires appreciation for both universal logistics principles and local operational realities. As Mexico continues developing its position in global supply chains, effective inventory practices will remain essential for businesses seeking to compete successfully in this dynamic market.