Essential Mobile Security Tips for Protecting Your Device and Data
In today's interconnected world, mobile devices have become repositories of our most sensitive information. From banking details to personal photos, the data stored on smartphones demands robust protection. As cyber threats evolve, understanding and implementing proper mobile security measures has never been more crucial for safeguarding your digital life.
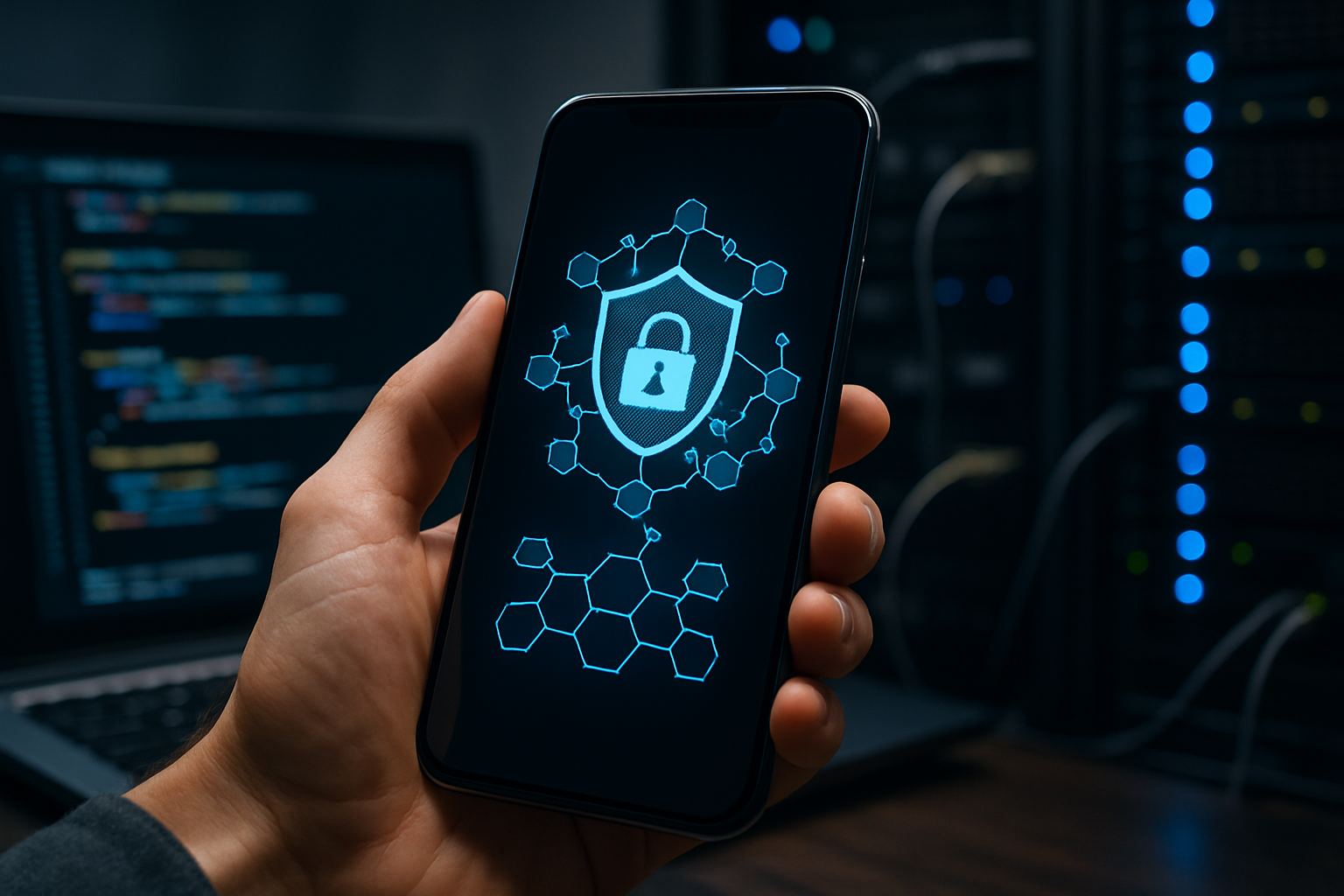

Mobile devices have become essential tools in our daily lives, serving as our communication hubs, work assistants, entertainment centers, and financial management tools. With this increased reliance comes heightened security risks, as smartphones and tablets now contain vast amounts of sensitive personal and professional information. Protecting these devices from various threats is no longer optional but necessary for everyone who owns a mobile device.
How to Keep Data Safe on Your Mobile Device
Data protection begins with understanding what information your device stores and how it might be vulnerable. Most smartphones contain personal photos, contact information, banking apps, emails, and possibly work-related documents. To keep this data safe, enable device encryption, which scrambles information so it can’t be read without the proper key. Most modern smartphones offer encryption options in their security settings.
Regular backups are another crucial aspect of data protection. By backing up your information to cloud services or external storage, you ensure that even if your device is lost, stolen, or compromised, your data remains recoverable. Consider using automatic backup features that work in the background while your device is charging and connected to Wi-Fi.
Finally, be mindful of the permissions you grant to applications. Many apps request access to your contacts, location, camera, or microphone. Review these permissions regularly and revoke access for apps that don’t genuinely need these features to function properly. This simple practice can significantly reduce data exposure risks.
Advanced Protection Strategies for Smartphones
Beyond basic security measures, several advanced strategies can enhance your smartphone’s protection. Two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an extra verification step when logging into accounts, typically requiring something you know (password) and something you have (a code sent to your device). Implementing 2FA on your email, banking, and social media accounts creates a substantial barrier against unauthorized access.
Biometric security features like fingerprint scanning, facial recognition, and iris scanning offer convenient yet robust protection for device access. These technologies are increasingly sophisticated and difficult to bypass compared to traditional PIN codes or patterns, though they should be used in conjunction with strong passwords rather than as replacements.
Consider installing a reputable mobile security app that provides real-time scanning for malware, suspicious links, and compromised Wi-Fi networks. These applications often include additional features like anti-theft tools, privacy advisors, and secure browsing options that complement your device’s built-in security measures.
Mobile Security for Every Type of Device
Security needs vary across different mobile platforms and device types. iOS devices benefit from Apple’s closed ecosystem, which restricts app installation to the official App Store, reducing malware risks. However, iOS users should still keep their operating systems updated and use strong Apple ID passwords with two-factor authentication.
Android devices offer more customization but may face increased security challenges due to the open nature of the platform. Android users should be particularly vigilant about downloading apps only from trusted sources like Google Play, checking app permissions carefully, and considering security solutions specifically designed for Android’s unique architecture.
Tablets and other mobile devices often share operating systems with smartphones but may have different usage patterns. If you use tablets primarily at home, configure them with stricter security settings since they don’t need the same on-the-go functionality as smartphones. For work tablets, investigate if your organization offers mobile device management solutions that can remotely enforce security policies and wipe data if necessary.
How to Stay Secure While Using Mobile Apps
Mobile apps represent one of the most significant security vulnerabilities on smartphones. Before downloading any app, research the developer, read reviews, and verify that the app has a legitimate purpose. Be wary of apps that request excessive permissions or those that offer services that seem too good to be true.
Regularly update your apps to ensure you have the latest security patches. Developers frequently release updates that address newly discovered vulnerabilities. Consider enabling automatic updates for your apps to ensure you’re always running the most secure versions available.
Be particularly cautious with financial apps and those that handle sensitive information. Use apps provided directly by your financial institutions rather than third-party alternatives. When making in-app purchases or entering payment information, verify that you’re using secure connections (look for HTTPS in web interfaces) and consider using payment services that mask your actual credit card details.
Mobile Security Best Practices for Public Networks
Public Wi-Fi networks present significant security risks for mobile users. These networks are often unencrypted, allowing potential attackers to intercept data transmitted between your device and the internet. When using public Wi-Fi, avoid accessing sensitive accounts or entering passwords and personal information.
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) creates an encrypted tunnel for your data, making it much more difficult for others to intercept your information. Consider installing a reputable VPN app on your mobile device and activating it whenever you connect to public or unfamiliar networks.
Another option is to use your mobile data connection instead of public Wi-Fi for sensitive tasks. While this may consume your data allowance, cellular connections are generally more secure than public Wi-Fi networks. If you frequently need secure connections while traveling, consider a portable Wi-Fi hotspot with proper security configurations.
Mobile security isn’t a one-time setup but an ongoing practice that requires awareness and adaptation as technology and threats evolve. By implementing these strategies across your devices, you can significantly reduce your vulnerability to common mobile security threats and protect your valuable personal and professional information.