Unlocking Efficiency: The Role of Warehouse Services in Modern Logistics
In today's fast-paced commercial environment, efficient logistics operations depend heavily on well-organized warehouse services. These facilities serve as critical nodes in supply chains, managing inventory, processing orders, and ensuring timely distribution of goods. As businesses expand their reach and consumer expectations grow, warehouse services have evolved from simple storage spaces into sophisticated operations centers that integrate technology, strategic planning, and specialized handling procedures to keep products moving smoothly from manufacturers to end users.
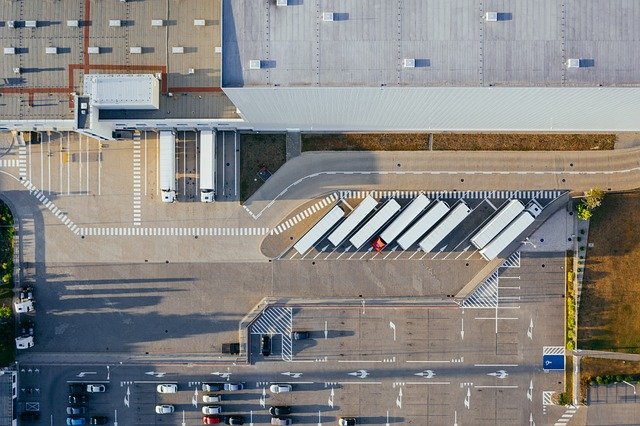

Modern supply chains rely on interconnected systems where warehouse services play a pivotal role in maintaining flow and efficiency. These facilities have transformed significantly over recent decades, adapting to changing market demands, technological advancements, and globalization. Understanding how warehouse services function within logistics networks helps businesses optimize their operations and meet customer expectations in competitive markets.
Understanding How Warehouse Services Support Supply Chains
Warehouse services form the backbone of supply chain operations by providing essential storage and distribution capabilities. These facilities act as buffer zones between production and consumption, allowing businesses to manage inventory levels effectively while responding to fluctuating demand patterns. By consolidating products from multiple sources and redistributing them according to customer orders, warehouses create efficiency in transportation and reduce overall logistics costs.
The strategic placement of warehouse facilities enables businesses to position inventory closer to target markets, reducing delivery times and transportation expenses. This geographical advantage becomes particularly important for companies serving diverse regions or managing seasonal demand variations. Warehouse services also provide the flexibility needed to handle unexpected market changes, allowing businesses to adjust inventory levels without disrupting production schedules or customer commitments.
Beyond basic storage functions, modern warehouse services contribute to supply chain visibility and control. Through integrated management systems, businesses can track inventory movements, monitor stock levels in real time, and coordinate activities across multiple locations. This transparency helps identify potential bottlenecks, optimize resource allocation, and improve decision-making throughout the logistics network.
An Overview of Common Warehouse Service Functions
Warehouse operations encompass a wide range of activities designed to manage goods efficiently from receipt to dispatch. Receiving functions involve unloading shipments, verifying quantities and quality, and updating inventory records. Proper receiving procedures ensure accuracy from the outset, preventing discrepancies that could affect downstream operations.
Storage and inventory management represent core warehouse functions, requiring systematic organization of products based on factors such as demand frequency, handling requirements, and storage conditions. Many facilities employ specialized storage systems including pallet racking, shelving units, and climate-controlled areas to accommodate different product types. Effective space utilization maximizes capacity while maintaining accessibility for order fulfillment activities.
Order processing and picking operations translate customer demands into physical actions, with warehouse staff retrieving items according to order specifications. Various picking methods exist, from manual selection to automated systems, each suited to different operational scales and product characteristics. Packing and shipping functions prepare orders for transportation, ensuring proper protection and documentation for delivery to final destinations.
Value-added services have become increasingly common in warehouse operations, including product assembly, labeling, customization, and quality inspection. These activities allow businesses to postpone final product configuration until closer to the point of sale, reducing inventory complexity and improving responsiveness to customer preferences. Returns processing represents another important function, managing reverse logistics flows and determining appropriate disposition for returned merchandise.
How Warehouse Services Are Used in Modern Logistics
Contemporary logistics strategies increasingly rely on warehouse services to support complex distribution models. E-commerce growth has particularly influenced warehouse operations, with facilities adapting to handle high volumes of small, individual orders rather than bulk shipments. This shift requires different layouts, equipment, and processes compared to traditional wholesale distribution models.
Many businesses utilize warehouse services through various operational models depending on their specific needs and resources. Some companies operate dedicated facilities tailored to their unique requirements, while others engage third-party logistics providers offering shared warehouse space and services. This flexibility allows businesses to scale operations according to demand without committing to long-term infrastructure investments.
Technology integration has revolutionized how warehouse services function within modern logistics networks. Warehouse management systems coordinate activities, optimize workflows, and provide data analytics for continuous improvement. Automated equipment including conveyor systems, sorting machines, and robotic picking devices increases processing speed and accuracy while reducing labor requirements for repetitive tasks.
Cross-docking operations represent an advanced warehouse service approach where incoming goods are immediately transferred to outbound transportation with minimal storage time. This strategy reduces handling costs and accelerates product flow, particularly beneficial for perishable items or time-sensitive shipments. However, cross-docking requires precise coordination between inbound and outbound logistics to function effectively.
Warehouse services also support inventory optimization strategies such as just-in-time delivery, where facilities maintain minimal stock levels and coordinate closely with suppliers and customers to synchronize material flows. This approach reduces carrying costs and storage requirements but demands reliable transportation networks and responsive warehouse operations to prevent stockouts.
The Evolution of Warehouse Service Standards
Quality standards and certifications have become increasingly important in warehouse operations as businesses seek reliable partners for their logistics needs. Various industry-specific requirements govern handling procedures, safety protocols, and documentation practices, particularly for regulated products such as pharmaceuticals, food items, and hazardous materials.
Sustainability considerations now influence warehouse service design and operations, with facilities implementing energy-efficient lighting, renewable power sources, and waste reduction programs. Green building certifications and environmental management systems demonstrate commitment to responsible operations while potentially reducing operating costs through resource efficiency.
Workforce development remains crucial for effective warehouse services, requiring ongoing training in safety procedures, equipment operation, and technology systems. As automation increases, human roles shift toward supervision, problem-solving, and exception handling rather than purely physical tasks. Maintaining skilled, motivated personnel ensures consistent service quality and operational reliability.
Conclusion
Warehouse services constitute essential components of modern logistics systems, providing the infrastructure and capabilities needed to manage product flows efficiently. From basic storage functions to sophisticated value-added services, these facilities enable businesses to meet customer demands while controlling costs and maintaining supply chain flexibility. As technology continues advancing and market conditions evolve, warehouse services will remain critical to successful logistics operations, adapting to support new business models and distribution strategies. Understanding the role and capabilities of warehouse services helps businesses make informed decisions about their logistics networks and operational approaches.