Unlocking Efficiency: The Role of Warehouse Services in Modern Logistics
Modern supply chains depend on sophisticated warehouse services to keep goods moving efficiently from manufacturers to consumers. These facilities have evolved far beyond simple storage spaces, now serving as dynamic hubs that coordinate inventory management, order fulfillment, and distribution activities. Understanding how warehouse services function within today's logistics networks helps businesses optimize their operations and meet growing customer expectations for speed and reliability.
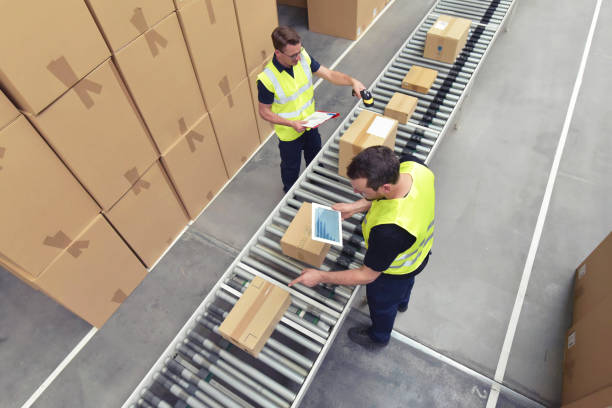

Warehouse services form the backbone of contemporary supply chain operations, enabling businesses to store, manage, and distribute products with precision and efficiency. As e-commerce continues to expand and consumer expectations rise, the importance of well-organized warehouse operations has never been greater. These facilities serve multiple functions beyond basic storage, including inventory control, order processing, packaging, and distribution coordination.
The integration of technology into warehouse operations has transformed how goods move through the supply chain. Modern facilities utilize warehouse management systems, automated equipment, and data analytics to optimize every aspect of their operations. This technological advancement allows businesses to reduce costs, improve accuracy, and respond quickly to market demands while maintaining high service levels.
Understanding How Warehouse Services Support Supply Chains
Warehouse services play a critical role in connecting manufacturers, distributors, and retailers within the supply chain ecosystem. These facilities act as strategic buffer points where products can be stored temporarily before moving to their final destinations. By positioning warehouses in optimal locations, companies can reduce transportation costs and delivery times while maintaining adequate inventory levels to meet customer demand.
The support provided by warehouse services extends to inventory management, where sophisticated tracking systems monitor stock levels in real time. This visibility allows businesses to make informed decisions about reordering, allocation, and distribution. Warehouse operations also facilitate cross-docking activities, where incoming shipments are quickly sorted and redirected to outbound transportation without long-term storage, significantly reducing handling time and costs.
Additionally, warehouse services provide value-added functions such as quality control inspections, product customization, kitting, and assembly. These activities enable businesses to postpone final product configuration until closer to the point of sale, improving flexibility and reducing the risk of holding obsolete inventory. The ability to perform these functions within warehouse facilities streamlines operations and creates efficiencies throughout the supply chain.
An Overview of Common Warehouse Service Functions
Warehouse facilities perform numerous essential functions that keep supply chains operating smoothly. Receiving operations involve unloading incoming shipments, verifying quantities and condition, and updating inventory records. This initial step ensures accuracy from the moment goods enter the facility and sets the foundation for all subsequent activities.
Storage and inventory management represent core warehouse functions, with products organized systematically to maximize space utilization and facilitate efficient retrieval. Modern warehouses employ various storage methods including pallet racking, shelving systems, and automated storage and retrieval systems. Inventory control processes track product movement, monitor expiration dates for perishable goods, and conduct regular cycle counts to maintain accuracy.
Order fulfillment encompasses picking, packing, and shipping activities that transform customer orders into delivered packages. Warehouse staff or automated systems retrieve items from storage locations, verify accuracy, package products appropriately, and prepare shipments for carrier pickup. This process requires careful coordination to ensure orders are completed correctly and dispatched promptly, directly impacting customer satisfaction.
Returns processing, also known as reverse logistics, handles products coming back into the warehouse from customers or retailers. This function includes inspecting returned items, determining their disposition, updating inventory records, and either restocking usable products or routing damaged goods for disposal or refurbishment. Effective returns management recovers value from returned merchandise and maintains inventory accuracy.
How Warehouse Services Are Used in Modern Logistics
In contemporary logistics networks, warehouse services have evolved to support increasingly complex distribution strategies. Multi-channel retailers rely on warehouses to fulfill orders from physical stores, e-commerce platforms, and wholesale customers simultaneously. This omnichannel approach requires flexible warehouse operations capable of handling diverse order profiles and shipping requirements efficiently.
Many businesses now utilize third-party logistics providers to access warehouse services without investing in their own facilities. These partnerships allow companies to scale operations quickly, enter new markets, and leverage specialized expertise in warehouse management. Third-party providers often operate multiple facilities across different regions, giving clients broader geographic coverage and improved delivery speed to end customers.
Warehouse services also support just-in-time inventory strategies, where products arrive at facilities shortly before they are needed for production or sale. This approach minimizes inventory holding costs and reduces the risk of obsolescence, but requires precise coordination between warehouse operations and transportation schedules. Advanced planning systems and real-time communication enable warehouses to execute these time-sensitive activities successfully.
The integration of automation technologies continues to reshape how warehouse services operate within modern logistics. Robotic systems, conveyor networks, and automated guided vehicles handle repetitive tasks with speed and consistency, while warehouse management software orchestrates activities and optimizes resource allocation. These technological investments improve productivity, reduce labor costs, and enhance accuracy, making warehouse operations more competitive and responsive to market demands.
Sustainability considerations increasingly influence warehouse service operations, with facilities implementing energy-efficient lighting, solar power systems, and waste reduction programs. Green building certifications and environmentally responsible practices appeal to environmentally conscious customers and help companies meet corporate sustainability goals while potentially reducing operating costs.
Conclusion
Warehouse services remain essential components of effective logistics strategies, providing the infrastructure and capabilities needed to manage product flow efficiently. From inventory management and order fulfillment to value-added services and returns processing, these facilities enable businesses to meet customer expectations while controlling costs. As technology continues advancing and supply chains grow more complex, warehouse services will adapt and evolve, maintaining their central role in connecting production with consumption across global markets.