Medical Assistant Programs Explained for Students in India
Students in India who are curious about working in clinics, hospitals, or diagnostic centres often hear about medical assistant courses but may not be sure what they really involve. Understanding how these programs work, what skills they teach, and what to expect during training can make it easier to choose the right learning path with confidence.

Many students in India are drawn to healthcare because it offers people-focused work and the chance to support doctors, nurses, and patients. Medical assistant programs are one path into this environment, combining basic clinical skills with administrative knowledge so learners can contribute to day-to-day operations in different healthcare settings. Knowing how these programs are structured helps students make informed decisions about their education.
In India, medical assisting is usually offered as a vocational or paramedical course rather than a standard university degree. Program names may vary, such as “medical assistant,” “patient care assistant,” or “clinical assistant,” but the core idea is similar: to prepare learners for supportive roles in healthcare teams by building both technical and communication skills.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
Learn essential medical skills
A central goal of any medical assistant program is to help students learn essential medical skills in a structured and supervised environment. Training generally begins with foundational subjects like human anatomy, basic physiology, and medical terminology. These topics give learners a clearer understanding of the body, common conditions, and the language used by healthcare professionals.
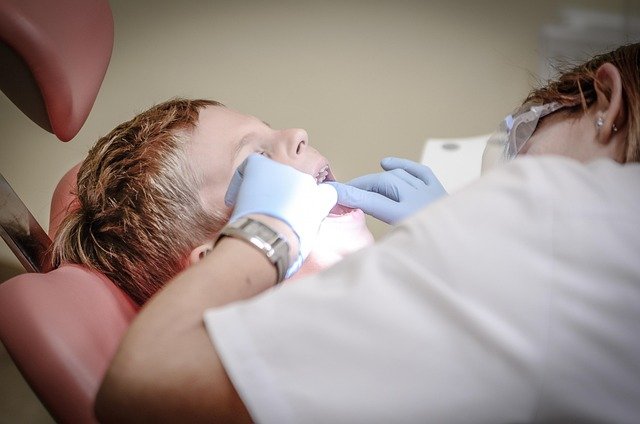
Most programs then move into practical skills required in clinics or hospitals. These may include measuring vital signs such as pulse, blood pressure, temperature, and respiratory rate; preparing patients for examinations; assisting with minor procedures; maintaining patient records; and following infection prevention and control practices. Students are also introduced to concepts of hygiene, sterilisation, and safe handling of instruments.
Communication and soft skills are another important part of training. Learners practice speaking with patients respectfully, explaining procedures in simple language, and working as part of a healthcare team. Many institutes also include basic computer skills and training on electronic records, since hospitals and diagnostic centres increasingly rely on digital systems.
Medical assistant programs explained
Medical assistant programs in India can take different forms, including short-term certificates, one-year diplomas, or longer paramedical courses. The exact duration and curriculum depend on the institute and the type of qualification. Typically, students are expected to have completed at least Class 12, often with science subjects preferred, though some vocational programs may have more flexible entry criteria.
Classroom learning is usually combined with practical lab work, where students handle equipment, simulate clinical situations, and practice procedures under guidance. For example, they may learn how to record patient histories, prepare examination rooms, manage simple dressings as permitted by local regulations, or assist with basic diagnostic tests. These activities are designed to improve both confidence and precision.
Many programs also include an internship or on-the-job training component in hospitals, clinics, or community health centres. During this period, students observe experienced staff, perform simple tasks under supervision, and gain a realistic sense of daily routines in healthcare facilities. This exposure helps them understand workplace expectations such as punctuality, teamwork, ethical conduct, and sensitivity to patient privacy.
Assessment methods often combine written examinations, practical evaluations, and internal assessments based on participation, assignments, and clinical performance. Successful completion typically requires consistent attendance, passing marks in theory and practicals, and satisfactory internship feedback where applicable.
How to become a medical assistant
For students in India wondering how to become a medical assistant, it can be helpful to think of the process as a series of clear steps, starting from school and moving through targeted training. The journey usually begins with completing secondary education. While science at the higher secondary level can be an advantage, some institutes may consider other streams, so carefully reading eligibility requirements is important.
The next step is researching programs in your area. Since course names, durations, and structures can differ, students often compare syllabus outlines, practical training opportunities, recognition of the certificate or diploma, and the overall reputation of the institution. Checking whether the program is affiliated with a recognised board, university, or skill council can provide additional assurance about its credibility.
Once a suitable course is identified, the admission process may include filling out application forms, submitting academic documents, and, in some cases, attending counselling sessions or basic aptitude assessments. After enrolment, students should be prepared for a schedule that balances theory classes, lab sessions, and, later, clinical exposure. Regular study, consistent practice of procedures, and active participation in skill labs can make the learning experience more effective.
Professional behaviour is also a key part of becoming a medical assistant. This includes respecting patient confidentiality, following instructions from supervisors, maintaining proper hygiene, and keeping accurate records. Many institutes emphasise ethics and responsible conduct, as these are central expectations in any healthcare setting.
Over time, some medical assistants may choose to deepen their expertise by pursuing additional certifications or related paramedical courses. Others may focus on particular areas such as outpatient care, diagnostic support, or administrative coordination, depending on their interests and the opportunities that align with their training.
A clear understanding of program structure, skill requirements, and day-to-day responsibilities helps students decide whether medical assistant training suits their strengths and long-term goals. By approaching this path with realistic expectations and a focus on learning, learners can build a solid foundation for contributing to healthcare teams in a variety of settings across India.