How US Teams Use AI to Automate Admin Work
Admin work can quietly consume hours each week across email, meetings, document handling, and routine reporting. Many US teams are using AI to reduce that load by drafting content, summarizing information, routing requests, and standardizing repetitive processes. The goal is usually not replacement, but faster turnaround times, fewer handoffs, and clearer records across common office workflows.
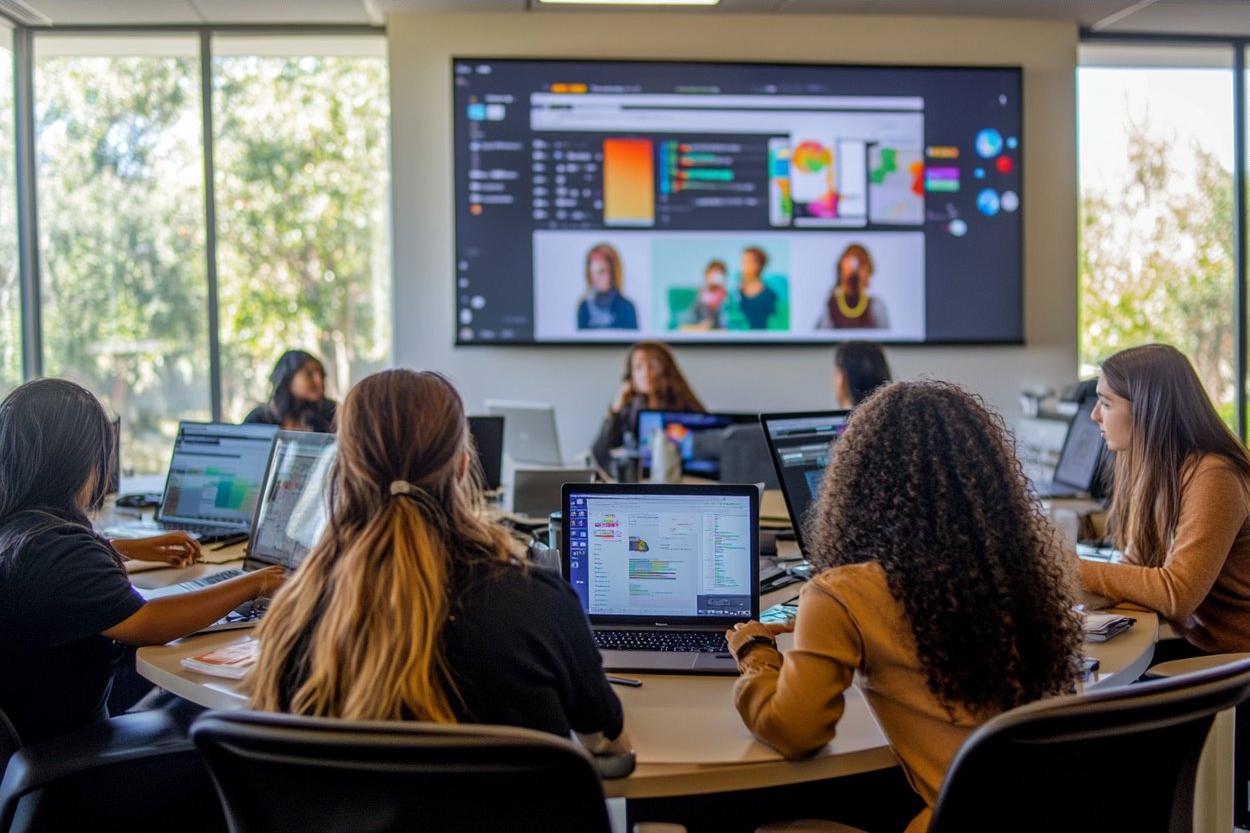

Everyday administrative work often expands to fill the calendar: responding to routine emails, preparing meeting notes, finding the latest version of a file, and copying updates between systems. US teams are increasingly using practical AI features inside tools they already use to reduce that friction. When implemented thoughtfully, automation can shorten cycle times, improve consistency, and free people to focus on decisions and customer-facing work rather than constant coordination.
AI tools used to improve everyday business tasks
Many teams start with low-risk tasks where errors are easy to spot and the time savings are immediate. Common examples include drafting first-pass emails, creating agenda templates, rewriting content for clarity, and producing short summaries of long threads or documents. AI is also used to turn unstructured notes into structured outputs such as action-item lists, follow-up messages, or status updates. In practice, the biggest gains often come from reducing context switching: instead of searching, copying, and reformatting, staff can request a draft and then edit it quickly.
Common applications of artificial intelligence software
Across operations, HR, sales, and finance, common applications of artificial intelligence software tend to cluster around text, meetings, and document workflows. Meeting assistants can generate transcripts, summarize discussion, and highlight decisions or open questions. Document and knowledge features can help employees find policies, previous proposals, or FAQs by asking natural-language questions rather than hunting through folders. In shared service environments, AI can support ticket triage by categorizing requests, suggesting responses, and routing work to the right queue, which helps reduce backlog without changing headcount.
How companies integrate AI tools into workflows
How companies integrate AI tools into workflows usually determines whether results feel transformative or merely experimental. The most effective approach is to map a process end to end, identify repetitive steps, and define what an acceptable AI output looks like. Teams often build simple guardrails such as approved prompt templates, required human review for external communications, and a short checklist for sensitive data. Integrations work best when AI is placed directly inside the system of record, so updates flow to the same places people already track work.
Another practical pattern is to treat AI as a co-worker for first drafts and a compiler for summaries, not as an autonomous decision-maker. For example, an operations coordinator might ask for a weekly status report draft sourced from meeting notes and project updates, then verify details before sending. Similarly, HR teams may use AI to standardize job description language or condense policy documents into employee-friendly summaries, while keeping final approvals with subject-matter owners. Measuring success with simple metrics like turnaround time, rework rates, and user adoption keeps the rollout grounded.
When selecting tools, many organizations evaluate providers already embedded in their communication and productivity stack, then add specialized options where needed. The comparison below highlights widely used products that support admin automation patterns such as drafting, summarizing, search, and workflow assistance.
| Provider Name | Services Offered | Key Features/Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Copilot | Productivity assistance in Microsoft 365 apps | Drafting and summarization in Word/Outlook, meeting and chat support in Teams, assistance across Office workflows |
| Google Gemini for Workspace | AI features in Google Workspace | Help with writing in Gmail/Docs, summarization, and assistance tied to Workspace content |
| OpenAI ChatGPT Enterprise | Enterprise conversational AI | Text drafting and analysis, workspace-style collaboration features, admin controls designed for business use |
| Slack AI | AI assistance inside Slack | Conversation summaries, search support, and faster catch-up on channels and threads |
| Zoom AI Companion | Meeting support in Zoom | Meeting summaries, highlights, and assistance features designed around video meetings |
| Atlassian Intelligence | AI in Jira and Confluence | Summaries, help drafting documentation, and support for project and knowledge workflows |
| Salesforce Einstein | AI in Salesforce platform | Assistance for sales and service workflows, automation support, and insights within CRM processes |
In day-to-day operations, the most sustainable wins come from clear boundaries: define which tasks can be automated, where humans must review, and how outputs are stored for accountability. Teams that standardize prompts, document “done” criteria, and keep AI outputs traceable typically see smoother adoption and fewer quality issues. Over time, AI becomes less of a novelty feature and more like an efficiency layer across routine admin work—especially when paired with good process design and consistent governance.