Hair Transplants: Latest Methods and Modern Approaches
Hair loss affects millions of people worldwide, prompting continuous advancements in restoration techniques. Modern hair transplantation has evolved significantly from its early days, offering more natural results, shorter recovery times, and improved patient comfort. Understanding the latest methods and approaches can help individuals make informed decisions about their hair restoration journey.
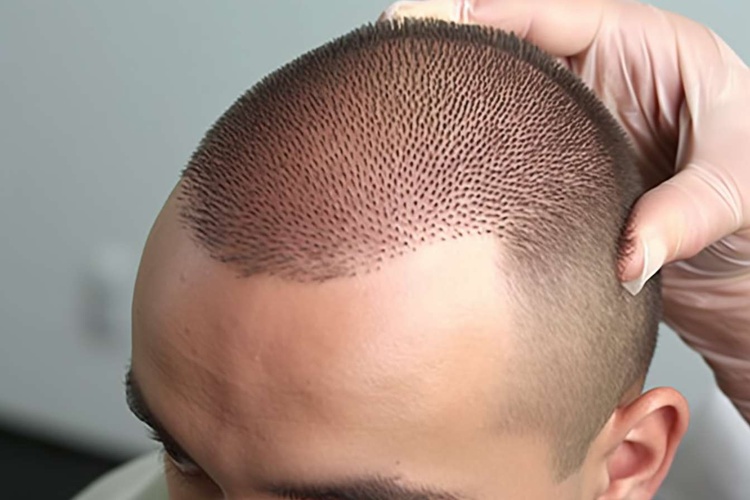
Hair transplantation has transformed dramatically over the past few decades, moving from outdated plug techniques to sophisticated procedures that deliver remarkably natural-looking results. Today’s methods prioritize minimal scarring, faster healing, and hairlines that blend seamlessly with existing hair. As technology advances and surgical expertise grows, patients have access to options that were unimaginable just years ago.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
What Are the New Approaches in Hair Transplantation?
Modern hair transplantation centers around two primary techniques: Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE). FUT involves removing a strip of scalp from the donor area, typically the back of the head, then dissecting it into individual follicular units for transplantation. While this method can harvest a large number of grafts in one session, it leaves a linear scar that may be visible with short hairstyles.
FUE, on the other hand, extracts individual follicular units directly from the scalp using a small punch tool. This approach leaves tiny, scattered scars that are virtually undetectable, making it ideal for patients who prefer shorter haircuts. Recent refinements in FUE include robotic assistance and motorized punch devices that increase precision and reduce procedure time. Both methods continue to evolve, with surgeons developing hybrid approaches that combine the strengths of each technique based on individual patient needs.
Which Modern Techniques in Hair Transplantation Should You Know?
Beyond the foundational FUT and FUE methods, several innovative techniques have emerged that enhance outcomes and patient experience. Direct Hair Implantation (DHI) represents a refinement of FUE where extracted follicles are immediately implanted using a specialized pen-like device called a Choi implanter. This simultaneous extraction and implantation reduces the time follicles spend outside the body, potentially improving graft survival rates.
Sapphire FUE uses blades made from sapphire crystal rather than steel to create recipient sites. Proponents claim these blades create more precise incisions with less tissue trauma, leading to faster healing and reduced scarring. Another advancement is the use of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy alongside transplantation procedures. PRP involves extracting growth factors from the patient’s own blood and applying them to the scalp to potentially enhance healing and stimulate hair growth in both transplanted and existing follicles.
Robotic-assisted hair transplantation systems use artificial intelligence and imaging technology to identify optimal donor follicles and create recipient sites with consistent depth and angle. While these systems represent significant technological investment, they can increase procedure efficiency and reduce human error during lengthy surgeries.
What Are the Latest Methods and Modern Approaches in Hair Transplants?
The newest developments in hair restoration extend beyond surgical technique to include regenerative medicine approaches. Stem cell therapy and hair cloning research aim to multiply donor follicles or generate entirely new hair growth, though these methods remain largely experimental and are not yet widely available for clinical use.
Micrografting techniques have become increasingly refined, with surgeons now routinely transplanting single-hair follicular units along the hairline to create the most natural appearance possible. The artistry involved in designing hairlines that match facial features and age appropriately has become as important as the technical aspects of the procedure itself.
Body hair transplantation has also gained traction as a solution for patients with limited scalp donor supply. Hair from the chest, back, or beard can be harvested and transplanted to the scalp, though these follicles often have different characteristics than scalp hair. Combining multiple donor sites allows surgeons to maximize coverage for patients with extensive hair loss.
Understanding Hair Transplantation Costs and Provider Options
The cost of hair transplantation varies significantly based on technique, geographic location, surgeon experience, and the number of grafts required. In Canada, FUE procedures typically range from 5 to 10 Canadian dollars per graft, while FUT may cost slightly less at 4 to 8 dollars per graft. A typical procedure requiring 2,000 to 3,000 grafts could therefore cost between 8,000 and 30,000 Canadian dollars.
| Technique | Average Cost per Graft (CAD) | Typical Session Cost (CAD) | Recovery Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| FUE | 5-10 | 10,000-30,000 | 7-10 days |
| FUT | 4-8 | 8,000-24,000 | 10-14 days |
| DHI | 6-12 | 12,000-36,000 | 7-10 days |
| Sapphire FUE | 6-11 | 12,000-33,000 | 7-10 days |
| Robotic FUE | 7-12 | 14,000-36,000 | 7-10 days |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Many clinics offer financing options to make procedures more accessible, and some patients choose to travel internationally for more affordable options, though this requires careful research into clinic credentials and surgeon qualifications.
How to Choose the Right Hair Transplantation Approach
Selecting the appropriate technique depends on multiple factors including the extent of hair loss, donor hair availability, budget, lifestyle considerations, and personal preferences regarding scarring. Patients who prefer wearing their hair very short may prioritize FUE or DHI methods that avoid linear scarring, while those seeking maximum graft yield in a single session might consider FUT.
Consultation with a qualified hair restoration surgeon is essential for developing a personalized treatment plan. During this consultation, the surgeon should assess hair loss patterns, examine donor area density, discuss realistic expectations, and explain the advantages and limitations of each technique. Viewing before-and-after photos of previous patients with similar hair characteristics can provide valuable insight into potential results.
Patients should also inquire about the surgeon’s experience with specific techniques, the credentials of the medical team, and the clinic’s infection control protocols. Reputable surgeons will be transparent about success rates, potential complications, and revision policies.
Conclusion
Hair transplantation continues to advance with new techniques and technologies that improve results and patient satisfaction. From refined FUE methods to robotic assistance and regenerative therapies, today’s options offer hope for those experiencing hair loss. Understanding the latest approaches, their costs, and how to select the right procedure empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their hair restoration journey. As research progresses and techniques evolve, the future of hair transplantation promises even more effective and accessible solutions for restoring natural-looking hair.