"Exploring Modular Homes: The Future of Modern Housing Development"
Modular homes are transforming the housing landscape across Canada, offering an innovative alternative to traditional construction methods. These factory-built structures combine efficiency, quality control, and design flexibility to meet the evolving needs of homeowners. As housing costs continue to rise and construction timelines extend, modular construction presents a compelling solution that addresses both affordability and speed without compromising on quality or customization options.
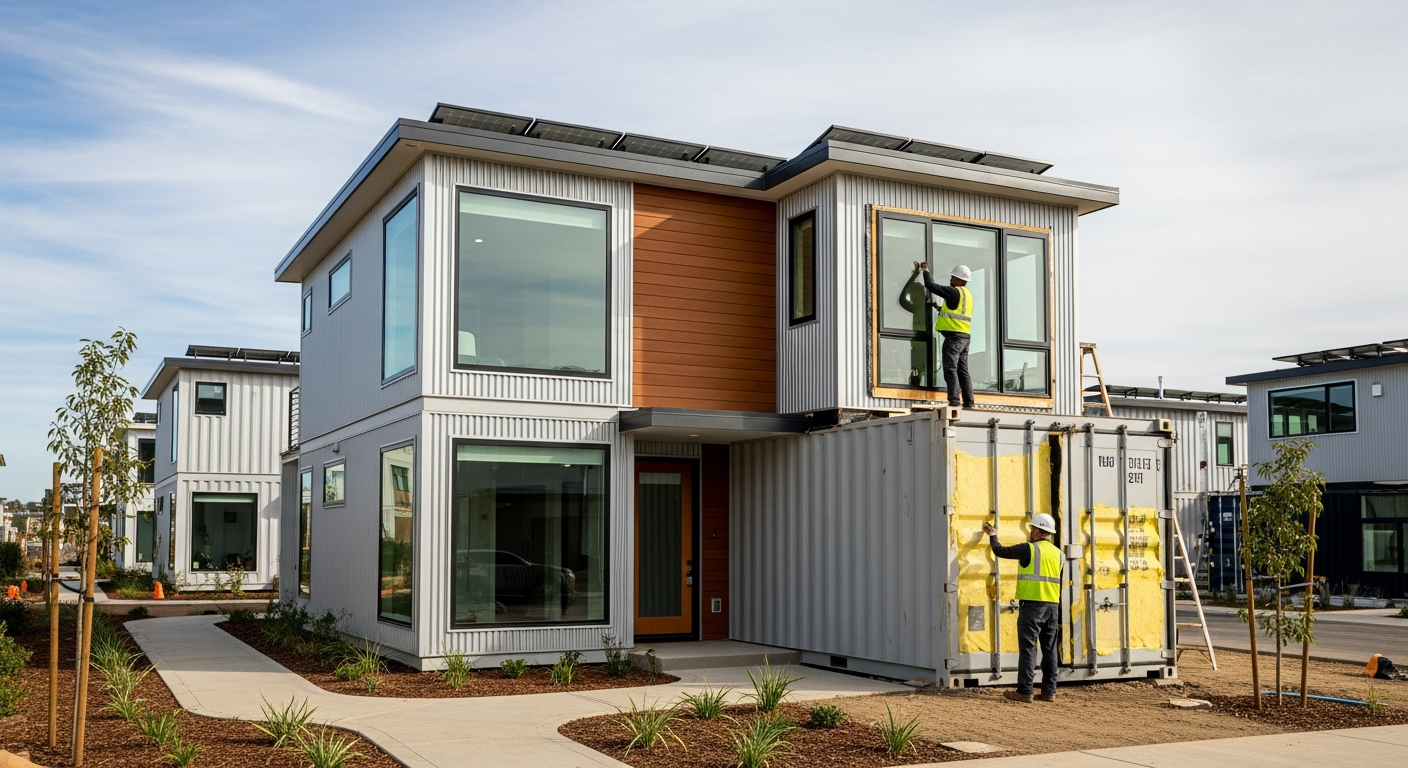

The housing market in Canada has experienced significant shifts in recent years, with buyers and builders alike seeking more efficient and cost-effective construction methods. Modular homes have emerged as a practical response to these challenges, representing a fundamental shift in how residential properties are designed, manufactured, and assembled. Unlike conventional site-built homes, modular construction takes place primarily in controlled factory environments, where precision and efficiency drive the building process.
Modular Homes Explained
Modular homes are permanent residential structures built in sections, or modules, within a factory setting before being transported to their final location for assembly. Each module is constructed to meet the same building codes and standards as traditional homes, ensuring structural integrity and safety. The term “modular” refers to the construction method rather than the quality or appearance of the home. Once assembled on-site, modular homes are virtually indistinguishable from their site-built counterparts. These structures are permanently affixed to foundations and are considered real property, qualifying for traditional mortgage financing and appreciating in value similarly to conventional homes.
How Modular Homes Fit Into Modern Housing Development
The integration of modular construction into contemporary housing development addresses several pressing challenges facing the Canadian real estate market. Labor shortages in the construction industry have created bottlenecks in traditional building projects, while weather-related delays can extend construction timelines significantly. Modular construction mitigates these issues by moving the majority of the building process indoors, where work can continue year-round regardless of weather conditions. This approach also reduces waste, as factory settings allow for more precise material management and recycling programs. Modern housing developments increasingly incorporate modular homes to meet tight deadlines and budget constraints while maintaining quality standards. The method proves particularly valuable in remote or northern communities where traditional construction faces additional logistical challenges.
How Modular Homes Work
The modular construction process begins with detailed design and planning phases, similar to traditional homes. Once plans are finalized, construction begins simultaneously on the building site and in the factory. While the foundation is prepared on-site, modules are built in the factory under controlled conditions. Each module includes framing, electrical wiring, plumbing, insulation, drywall, and often flooring and cabinetry. Quality control inspections occur at multiple stages throughout factory construction. When modules are complete, they are transported to the building site on flatbed trucks. Specialized cranes lift and position each module onto the prepared foundation, where they are secured together and to the foundation. The assembly process typically takes one to two days, after which finishing work connects utilities, seals joints between modules, and completes exterior elements. Final inspections ensure all building codes are met before occupancy.
Exploring the Basics of Modular Home Structures
Modular home structures are engineered to withstand the stresses of transportation and crane lifting, often making them stronger than traditional builds. The modules feature reinforced framing and additional structural supports designed to handle these unique demands. Common configurations include single-story ranch styles, two-story designs, and split-level layouts. Modules typically range from 12 to 16 feet wide and up to 60 feet long, though dimensions vary by manufacturer and transportation regulations. Multiple modules combine to create homes ranging from compact single-family dwellings to spacious multi-bedroom residences. Architectural flexibility allows for various exterior finishes, including vinyl siding, brick, stone, and stucco, enabling modular homes to match regional aesthetic preferences. Interior layouts can be customized during the design phase, offering choices in room configurations, finishes, and fixtures comparable to site-built homes.
Cost Considerations and Provider Comparisons
Understanding the financial aspects of modular homes helps potential buyers make informed decisions. Costs vary based on size, design complexity, location, and finish quality. Factory construction typically offers cost efficiencies through bulk material purchasing and streamlined labor processes. However, transportation and assembly costs must be factored into the total investment. Site preparation, foundation work, and utility connections add to the base module price. The following comparison provides general cost estimations for modular homes in Canada:
| Provider Type | Base Module Cost Range | Total Project Cost Range | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regional Manufacturers | $100,000 - $200,000 | $150,000 - $300,000 | Local delivery, standard designs, regional code compliance |
| National Builders | $120,000 - $250,000 | $180,000 - $400,000 | Wider design selection, established warranty programs, financing assistance |
| Custom Modular Companies | $150,000 - $350,000 | $225,000 - $550,000 | Architectural customization, premium finishes, unique layouts |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Advantages and Considerations
Modular construction offers several distinct advantages beyond cost and speed. The controlled factory environment protects building materials from weather exposure, reducing the risk of moisture-related issues like mold or wood rot during construction. Waste reduction through precise cutting and material reuse contributes to environmental sustainability. Energy efficiency often exceeds traditional builds due to tight construction tolerances and modern building techniques. However, prospective buyers should consider certain factors. Transportation limitations may restrict design options in remote areas or regions with narrow roads. Land acquisition and site preparation remain the buyer’s responsibility and can significantly impact total costs. Financing, while available through traditional mortgages, may require lenders familiar with modular construction. Zoning regulations vary by municipality, and some areas maintain restrictions on modular homes, making research essential before purchasing land.
The Future Outlook
The modular housing sector continues to evolve with technological advances and changing market demands. Innovations in materials, construction techniques, and design software expand possibilities for customization and efficiency. As housing affordability challenges persist across Canada, modular construction provides a viable pathway to homeownership for many families. The method’s adaptability makes it suitable for various applications, from single-family homes to multi-unit developments and even commercial structures. Growing acceptance among buyers, builders, and lenders suggests modular homes will play an increasingly significant role in addressing Canada’s housing needs while maintaining the quality and permanence expected in residential construction.