Emergency Generators for Home Power Backup Solutions
Power outages can strike without warning, leaving homes without electricity for hours or even days. Whether caused by severe weather, grid failures, or natural disasters, losing power disrupts daily life and can pose safety risks. Emergency generators provide a reliable solution to keep essential systems running when the grid goes down. Understanding how these backup power systems work, what types are available, and how to choose the right one can help homeowners maintain comfort and security during unexpected outages.
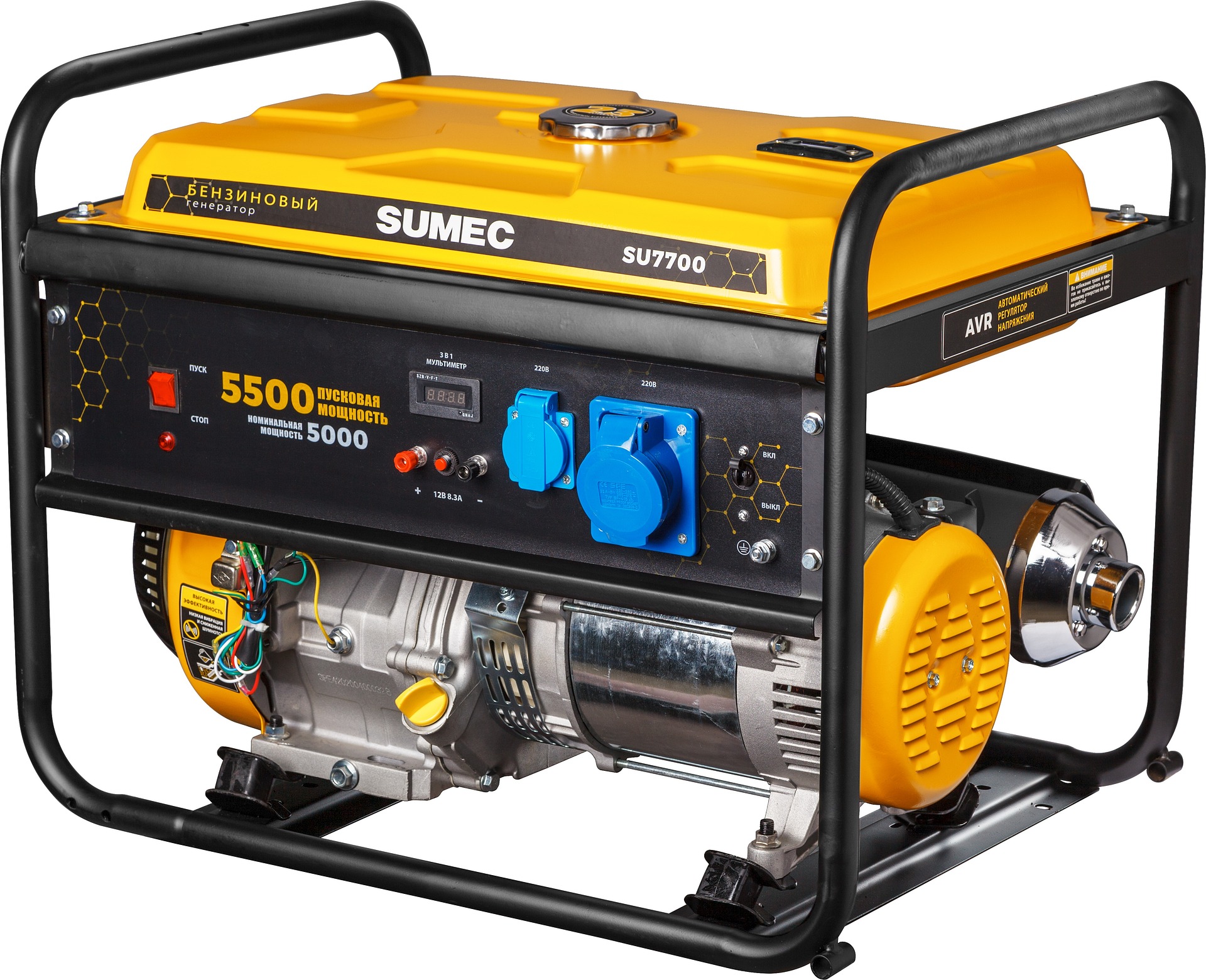

Understanding Home Backup Power Systems
Home backup generators serve as independent power sources that activate when utility electricity fails. These units convert fuel into electrical energy, supplying power to critical appliances, heating and cooling systems, medical equipment, and other necessities. Modern emergency generators range from portable units that power a few devices to whole-house systems that seamlessly take over when the main power supply is interrupted. The technology has advanced significantly, offering homeowners more efficient, quieter, and more reliable options than ever before.
The basic operation involves an engine that drives an alternator to produce electricity. Automatic transfer switches detect power loss and signal the generator to start, often within seconds of an outage. This automation ensures continuous power without manual intervention, which is particularly valuable during nighttime outages or when homeowners are away. Understanding the fundamental operation helps in selecting a system that matches specific household needs and budget constraints.
Stay Powered Anytime with the Right Generator Type
Homeowners can choose from several generator categories, each with distinct advantages. Portable generators offer flexibility and lower upfront costs, typically ranging from 3,000 to 10,000 watts. These units run on gasoline or propane and require manual setup during outages. They work well for powering select appliances and are popular for their mobility and affordability.
Standby generators represent a permanent installation solution, automatically activating during power failures. These systems connect directly to home electrical panels and fuel sources, usually natural gas or propane. Capacity ranges from 7,000 to 22,000 watts or more, sufficient to power entire homes. While initial investment is higher, the convenience and comprehensive coverage make them attractive for areas with frequent outages.
Inverter generators provide cleaner power suitable for sensitive electronics, operating more quietly than conventional models. These units adjust engine speed based on power demand, improving fuel efficiency. Hybrid models combine multiple fuel options, offering flexibility when one fuel type becomes scarce during extended emergencies.
Essential Energy Solution Sizing and Capacity
Proper generator sizing ensures adequate power without overspending on unnecessary capacity. Begin by listing essential appliances and systems that must remain operational during outages. Refrigerators typically require 600-800 watts running power with higher starting watts. Sump pumps, well pumps, heating systems, and medical equipment should be prioritized based on household needs.
A whole-house generator for a typical 2,000-square-foot home generally requires 15,000 to 20,000 watts. Smaller homes or those prioritizing only critical circuits may function well with 7,000 to 10,000 watts. Professional electricians can perform load calculations to determine precise requirements, accounting for starting watts that exceed running power demands for motors and compressors.
Oversizing leads to inefficient fuel consumption and higher costs, while undersizing results in inadequate power during critical moments. Most manufacturers provide sizing guides, but consulting with certified installers ensures accurate assessments tailored to specific home configurations and local electrical codes.
Installation Requirements and Safety Considerations
Professional installation is strongly recommended for standby generators, as they involve electrical panel connections, fuel line installation, and compliance with local building codes. Transfer switches must be properly installed to prevent backfeeding, which can endanger utility workers and damage equipment. Generators require adequate ventilation, as exhaust contains deadly carbon monoxide. Units must be positioned at least 20 feet from windows, doors, and air intakes.
Portable generators also pose carbon monoxide risks and should never operate indoors, in garages, or near building openings. Proper grounding prevents electrical shock hazards. Regular maintenance, including oil changes, filter replacements, and periodic testing, ensures reliable operation when needed. Many standby systems include self-diagnostic features and automatic weekly test cycles to maintain readiness.
Local permits are typically required for permanent installations. Homeowners associations may have restrictions on generator placement and noise levels. Checking these requirements before purchase prevents costly modifications or compliance issues.
Comparing Generator Options and Cost Considerations
When evaluating emergency generators, understanding the investment involved helps in making informed decisions. Costs vary significantly based on capacity, features, and installation complexity. Portable generators represent the most economical entry point, while whole-house standby systems require substantial upfront investment but offer comprehensive protection and convenience.
| Generator Type | Capacity Range | Estimated Cost | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Portable Generator | 3,000-10,000 watts | $400-$1,500 | Manual operation, gasoline or propane, mobile |
| Inverter Generator | 2,000-7,000 watts | $600-$3,000 | Quiet operation, clean power, fuel efficient |
| Home Standby Generator | 7,000-22,000 watts | $3,000-$6,000 (unit only) | Automatic activation, natural gas or propane, permanent installation |
| Installation Costs | Varies | $1,500-$5,000 | Includes transfer switch, electrical work, fuel connections |
| Annual Maintenance | N/A | $150-$300 | Professional servicing, parts, oil changes |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Fuel costs also factor into long-term ownership expenses. Natural gas offers convenience and continuous supply through utility lines, while propane requires tank refills but provides independence from utility infrastructure. Gasoline-powered portable units need fresh fuel rotation to prevent carburetor damage from stale fuel.
Warranty coverage varies by manufacturer, typically ranging from two to five years for residential units. Extended warranties and service contracts provide additional protection but increase overall costs. Evaluating total cost of ownership, including fuel, maintenance, and potential repairs, provides a complete financial picture.
Maintaining Readiness for Power Outages
Regular maintenance ensures generators function reliably during emergencies. Standby units benefit from monthly visual inspections and weekly automatic test runs that many models perform independently. Oil and filter changes follow manufacturer schedules, typically every 100-200 hours of operation or annually. Spark plugs, air filters, and fuel filters require periodic replacement.
Portable generators need more hands-on care, including fuel stabilizer addition when storing for extended periods. Battery maintenance for electric-start models prevents starting failures during outages. Keeping spare parts like spark plugs, oil, and filters on hand enables quick repairs without waiting for deliveries during widespread emergencies.
Documenting maintenance activities and keeping service records helps track system health and maintains warranty coverage. Many manufacturers offer maintenance reminders and support through mobile apps or online portals, simplifying the process for busy homeowners.
Conclusion
Emergency generators provide essential backup power that keeps homes functional and families safe during utility outages. From portable units offering basic coverage to comprehensive whole-house systems with automatic activation, options exist for various needs and budgets. Proper sizing, professional installation, and regular maintenance ensure these systems deliver reliable performance when needed most. By understanding the types available, evaluating capacity requirements, and considering long-term costs, homeowners can select backup power solutions that provide peace of mind and protection against the disruptions caused by power failures.